- Lis Software Vendors
- What Is Enterprise Software Vendors
- Software Vendor App
- What Is Software Suppliers
- Software Company
Definition of Vendor Management. Vendor management is the process that empowers an organization to take appropriate measures for controlling cost, reducing potential risks related to vendors, ensuring excellent service deliverability and deriving value from vendors in the long-run.This includes researching about the best suitable vendors, sourcing and obtaining pricing information, gauging the.
- An Independent Software Vendor (ISV) is a business or an individual that builds, develops and sells consumer or enterprise software that is consumed by end users. In other words, an Independent Software Vendor is a company whose main function is to distribute its software. Independent Software Vendors are also known as Software Publishers.
- A software producer that is not owned or controlled by a hardware manufacturer; a company whose primary function is to distribute software. Hardware manufacturers that distribute software (such as IBM and Unisys) are not ISVs, nor are users (such as banks) that may also sell software products.
- As the name would suggest, vendor risk management software is any software that helps you manage your company’s risk when it comes to vendors. Vendors can be anyone you have a.
- ISV is short for Independent Software Vendor, a phrase used to describe a company that only produces software.A hardware company that also produces software (IBM for example) is not considered an ISV.
A quality vendor performance review (a.k.a performance review) assesses how the vendor is performing against Key Performance Indicators (KPI)'s and Service Level Agreements (SLA)'s established in the vendor’s contract. It should also show non-contractual performance issues, such as incidents that aren't measured by a service level. For example, you can monitor incidents such as the vendor providing wrong information to customers or other poor customer service.

The goals of a performance review are to:
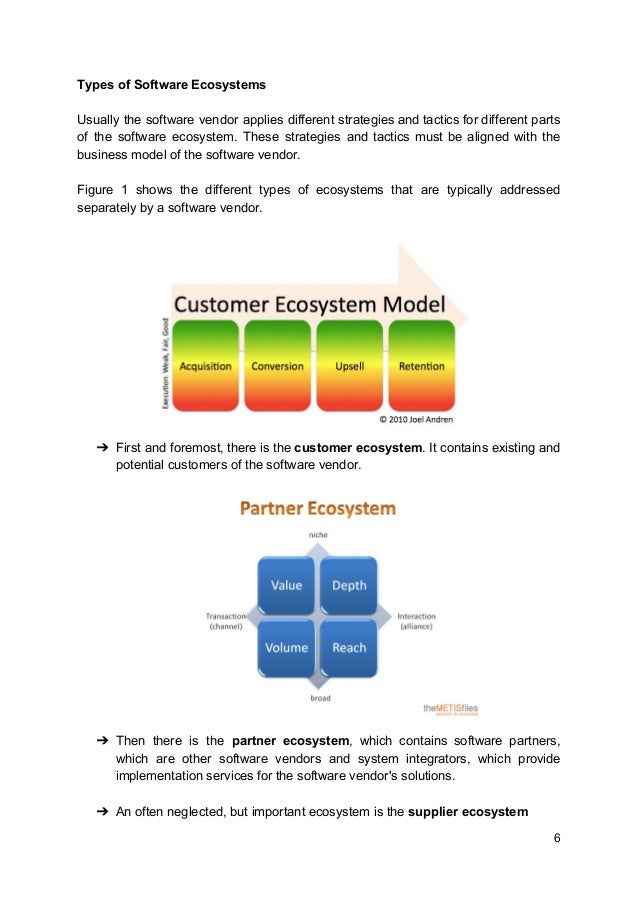
- Monitor compliance of contractually agreed upon KPI's and SLA's
- Identify areas where the vendor is not performing to expectations
- Partner with the vendor to resolve low vendor performance
- Benchmark the vendor's performance against similar vendors
- Assess performance trends and resolve prior to impacting productivity
- Partner with the business owner(s) to ensure they are engaged with and utilizing the vendor's services
Each performance review should have a scoring model that quantifies the performance level. A basic scoring model that I found sufficient was:
- 0 — Not Applicable
- 1 — Does Not Meet Expectations
- 2 — Needs Improvement
- 3 — Meets Expectations
- 4 — Exceeds Expectations
Why Should I Use Performance Reviews If I Have Scorecards?
Scorecards are one piece of a performance review that tracks the adherence of the agreed upon KPI's and SLA's compared to the larger picture of the vendor's overall performance. Scorecards will not capture all incidents or non-metric related issues such as your company's interaction with the vendor, billing issues or the overall quality of the vendor. Depending on the frequency of the reporting and the vendor's services, scorecards should be reviewed weekly or monthly. Performance reviews should be performed quarterly, semi-annually or annually depending on the vendor's services and their risk level.
Performance reviews may capture data from:
- Scorecards
- Incident reports
- Action plans
- Internal business owner(s)
- Customer surveys
- Prior performance reviews
- Performance reviews from similar vendors
Performance reviews are a perfect way to partner with the vendor for a successful relationship and to hold the vendor accountable for their performance. If you have not been using performance reviews and have older contracts, this is a perfect opportunity to assess the vendor's overall performance, negotiate better contracts with more defined SLA's and penalties.
How Often Should Performance Reviews Be Performed?
Initial Performance Review
As a general rule of thumb for new services, the initial performance review should be performed 90 days after the services are implemented. This will allow enough time to determine how the vendor is performing and tweak specific KPI's, SLA's and/or implement action plans. If the vendor is not performing to desired expectations prior to the 90 days, each occurrence should be documented as an incident and used in the performance review. If the incident creates a risk, it should be addressed immediately with the vendor by creating an action plan with a SMART (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, time-bound) goal that will be monitored by the Vendor Management Office (VMO).
Ongoing Performance Reviews
I have found that the best time to conduct a performance review is 180 days prior to the renewal notification notice, similar to the risk and diligence reviews. This normally gives ample time to identify performance gaps to review with the business owners prior to renewing the contract.
When gathering data for the review, it is always a great idea to review the prior performance review to look for negative trending. If the behavior is evident but not worth terminating the vendor, you may negotiate into the renewal penalties for poor performance and reference back to the trended history.
Using vendor management software to alert you on upcoming reviews is beneficial to the management of your vendors.
How Often Should Ongoing Reviews Be Conducted?
Reviews should be performed according to the vendor's type of service and the impact of the service if the KPI's or SLA's are not met. The frequency of the performance reviews should be set initially with the business owner and the vendor. The review frequency should never change if the vendor is not performing; instead incident tracking and action plans should be utilized for any performance issues between reviews.
- Annual Reviews — IT, HR, facility, non-customer impacting vendors
- Semi-Annual Reviews — Back office, indirect customer impacting vendors
- Quarterly Reviews — Customer impacting and high risk vendors
Who Should Be Included In the Review?
The Vendor Management Office (VMO) should conduct the meeting and include each business owner to review the vendor’s performance. During the meeting the VMO will objectively score the performance review based on feedback from the business owners. For each low score, the business owner(s) and VMO will decide if the vendor should be placed on an action plan, be put on notice or change the metric to be more realistic.
Lis Software Vendors
Once the internal review is complete, the VMO should work with the vendor to work through any low scores. The best way to resolve low scores is to have the vendor create an Action Plan. Partner with the vendor to track the vendor's progress to resolution with SMART goals to ensure both parties obtain the desired results.
What Is Enterprise Software Vendors
Base the Review Questions on the Type of Vendor

Vendor performance review forms should be broken down by the type of service the vendor performs. Their review form should merge specific KPI and SLA questions and generic questions such as: how many incidents the vendor had, how well is their training, etc.
I recommend that you have multiple performance review forms with specific KPI's and SLA's. With a good vendor management software system you should be able to create a review form with generic questions then copy the form to make service-specific review forms.
Below are four common categories that can be used to help shape your performance review efforts:
Software Vendor App
- Vendor Performance — Contractually agreed upon expectations such as:
- Key Performance Indicators — quantifiable measures used to determine efficiency and effectiveness of the service
- Service Level Agreement — formal negotiated agreement which defines parameters and responsibilities for the delivery of a service
- Vendor Incidents — any occurrence that disrupts the company’s operation
- Vendor Billing — accuracy and timeliness of billing
- Vendor Quality — overall vendor experience to include (this section is not KPI or SLA specific):
- Vendor responsiveness — responsiveness to general questions and follow-up
- Training quality – quality of training material used for both the vendor and the company
- Knowledge – knowledge of the vendor's core functions to include the vendor rep, customer service, IT and other departments
- Vendor innovation – knowledge and adaptability of its services
What Is Software Suppliers

Sample of Vendor Performance Review Questions
The following performance review is a sample that could be used for a vendor call center. Using vendor management software will make it easier to create review forms for specific services, as one review form will not work for all vendors.
| Vendor Performance |
|---|
| What is the vendor's inbound AHT in Customer Service for this review period? |
| What is the vendor's Average Speed of Answer in Customer Service for this review period? |
| What is the vendor's Customer Satisfaction score during this review period? |
| What is the vendor's First Call Resolution (FCR) score during this review period? |
| What is the vendor's employee attrition during this review period? |
| What is the vendor's right party connect (RPC) rate for Outbound Collections during this period? |
| Vendor Incidents |
| Provide the amount of incidents opened for the vendor during this review period. |
| Provide the number of incident closed in a timely manner by the vendor had during this review period. |
| Provide the number of incidents still open during this review period. |
| Provide the number of Action Plans the vendor had during this review period. |
| Provide the number of Action Plans successfully completed during this review period. |
| Provide the number of incidents that had a major impact on the business or customer during this review period. |
| Provide the number of Action Plans that had a major impact on the business or customer during this review period. |
| Vendor Quality |
| Rate the vendor's responsiveness to general questions and inquiries. |
| Rate the vendor's innovativeness to the services they provide. |
| Rate the vendor's knowledgeable regarding their service and how it relates to our business. |
| Rate the vendor's general accessibility to the business. |
| Rate the vendor's system as to its user-friendliness. |
| Vendor Billing |
| Has the vendor been contractually compliant with the fees charged during this review period? |
| Is the vendor timely on sending the invoices out during this review period? |
| Did the vendor duplicate invoices of individual charges during this review period? |
Software Company
Paul Boone is an experienced VMO manager. Connect with Paul on LinkedIn.
